
Understand various forming processes of metal materials (I): Casting
Material forming method is not only an important content of part design, but also an issue of great concern to manufacturers, but also a key factor in the process of material processing. Today, Xiaobian will take you to see various forming processes of metal materials.
1、 Casting
The production method of pouring liquid metal into the mold cavity corresponding to the shape and size of the part and waiting for it to cool and solidify to obtain the blank or part is usually called metal liquid forming or casting.
Process flow: liquid metal → mold filling → solidification shrinkage → casting.
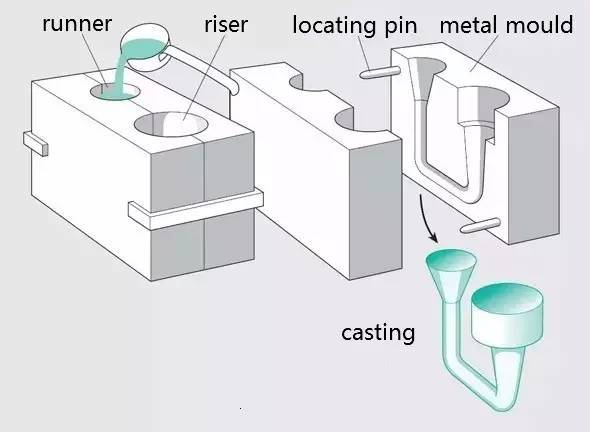
Process features:
1. It can produce products with arbitrary complex shape, especially those with complex inner cavity shape.
2. Strong adaptability, unlimited alloy types and almost unlimited casting size.
3. Wide sources of materials, remelting of waste products and low equipment investment.
4. High scrap rate, low surface quality and poor working conditions.
Casting classification:
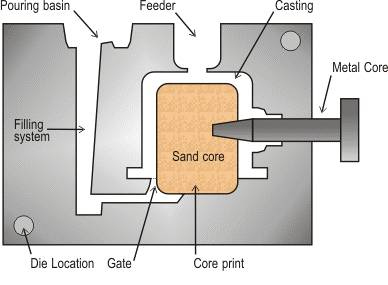
(1) Sand casting

Sand casting: a casting method for producing castings in sand molds. Steel, iron and most non-ferrous alloy castings can be obtained by sand casting.
Technological process:
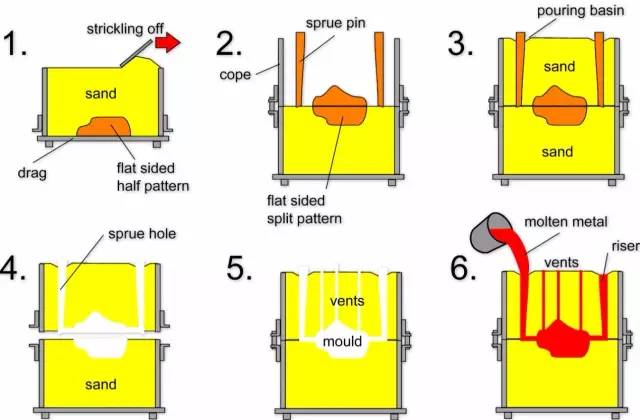
Technical features:
1. It is suitable for making blanks with complex shape, especially with complex inner cavity;
2. Wide adaptability and low cost;
3. For some materials with poor plasticity, such as cast iron, sand casting is the only forming process to manufacture their parts or blanks.
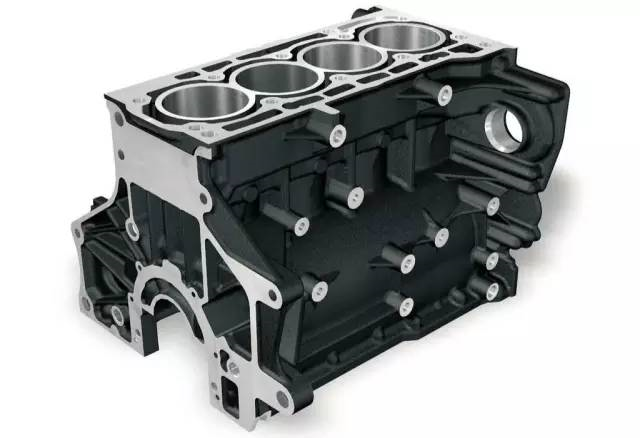
Application: automotive engine cylinder block, cylinder head, crankshaft and other castings
(2) Investment casting

Investment casting: it usually refers to the casting scheme that the pattern is made of fusible materials, coated with several layers of refractory materials on the surface of the pattern to make the mold shell, and then the pattern is melted out of the mold shell, so as to obtain the mold without parting surface, which can be filled with sand after high-temperature roasting. It is often called “lost wax casting”.
Process features:
Advantage:
1. During die casting, the metal liquid bears high pressure and fast flow rate
2. Good product quality, stable size and good interchangeability;
3. High production efficiency and many times of use of die casting die;
4. It is suitable for mass production and has good economic benefits.
Disadvantages:
1. Castings are prone to small pores and shrinkage porosity.
2. Die castings have low plasticity and are not suitable for working under impact load and vibration;
3. It can cast castings with complex appearance, and the cast alloy is not limited.
Disadvantages: complicated process and high cost
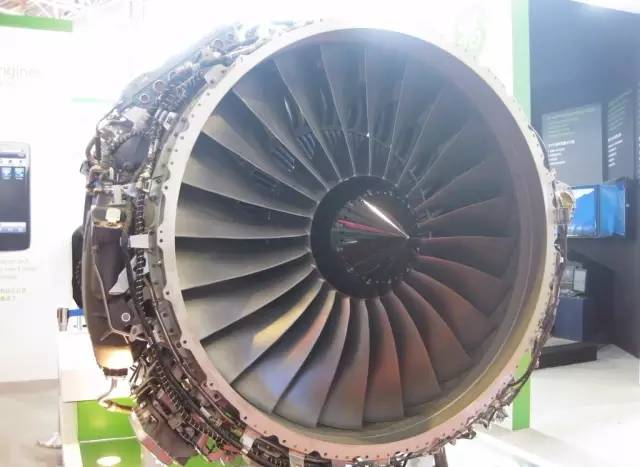
Application: it is suitable for producing small parts with complex shape, high precision requirements, or difficult to process, such as turbine engine blades.
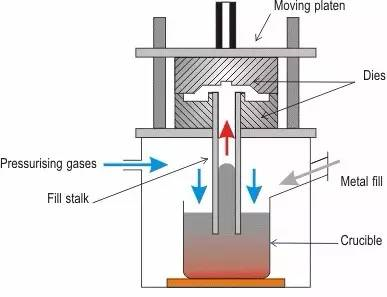
(3) Die casting
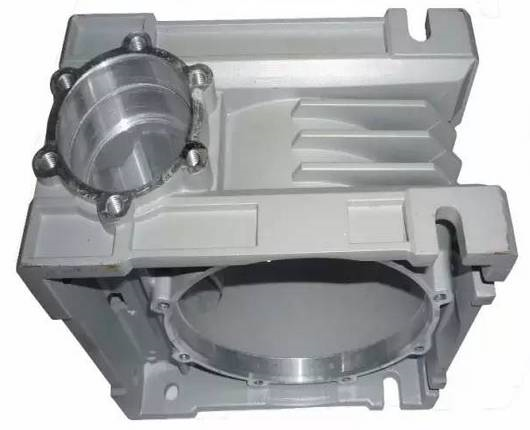

Die casting: high pressure is used to press the liquid metal into a precision metal mold cavity at high speed, and the liquid metal is cooled and solidified under pressure to form a casting.
Process features:
Advantage:
1. During die casting, the metal liquid bears high pressure and fast flow rate
2. Good product quality, stable size and good interchangeability;
3. High production efficiency and many times of use of die casting die;
4. It is suitable for mass production and has good economic benefits.
Disadvantages:
1. Castings are prone to small pores and shrinkage porosity.
2. Die castings have low plasticity and are not suitable for working under impact load and vibration;
3. During high melting point alloy die casting, the service life of the mold is low, which affects the expansion of die casting production.
Application: die castings were first used in automobile industry and instrument industry, and then gradually expanded to various industries, such as agricultural machinery, machine tool industry, electronic industry, national defense industry, computer, medical equipment, clocks, cameras and daily hardware.
(4) Low pressure casting
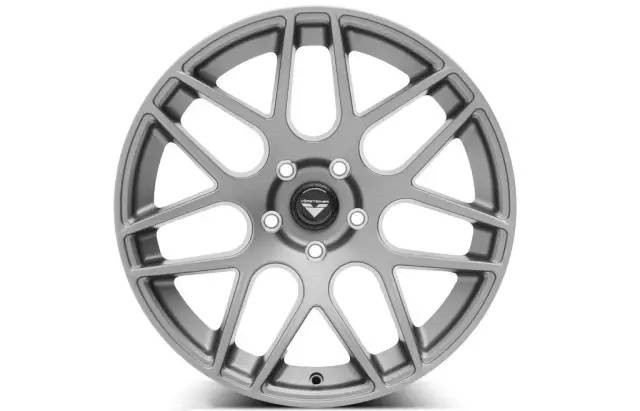

Low pressure casting: it refers to the method of making liquid metal fill the mold under the action of low pressure (0.02 ~ 0.06mpa) and crystallize under pressure to form castings.
Technological process:
Technical features:
1. The pressure and speed during pouring can be adjusted, so it can be applied to various casting molds (such as metal mold, sand mold, etc.), casting various alloys and castings of various sizes;
2. The bottom injection mold filling is adopted, the liquid metal mold filling is stable and free of splash, which can avoid the involvement of gas and the scouring of mold wall and core, and improve the qualified rate of castings;
3. The casting crystallizes under pressure, with compact structure, clear outline, smooth surface and high mechanical properties, which is particularly beneficial to the casting of large and thin-walled parts;
4. The feeding riser is omitted, and the metal utilization rate is increased to 90 ~ 98%;
5. Low labor intensity, good working conditions, simple equipment, easy to realize mechanization and automation.
Application: mainly traditional products (cylinder head, wheel hub, cylinder frame, etc.).
(5) Centrifugal casting

Centrifugal casting: a casting method in which liquid metal is poured into a rotating mold, filled with the mold under the action of centrifugal force and solidified.
Technological process:
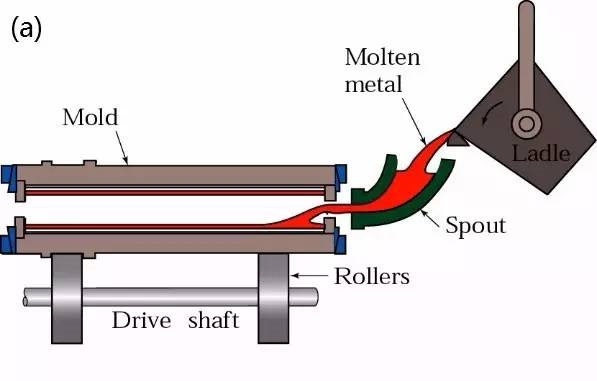
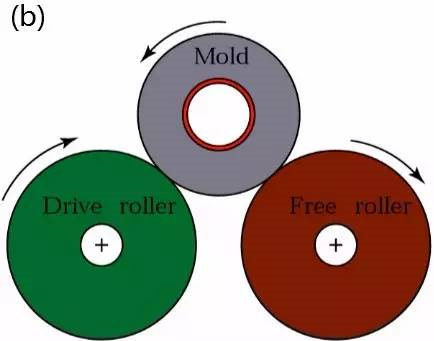
Process characteristics
Advantage:
1. There is almost no metal consumption of gating system and riser system, so as to improve the process yield;
2. The core can not be used in the production of hollow castings, so the metal filling capacity can be greatly improved in the production of long tubular castings;
3. The casting has high density, few defects such as pores and slag inclusion, and high mechanical properties;
4. It is convenient to manufacture barrel and sleeve composite metal castings.
Disadvantages:
1. There are some limitations in the production of special-shaped castings;
2. The inner hole diameter of the casting is inaccurate, the inner hole surface is rough, the quality is poor, and the machining allowance is large;
3. Castings are prone to specific gravity segregation.
Application:
Centrifugal casting was first used to produce cast pipes. Centrifugal casting technology is used in metallurgy, mining, transportation, drainage and irrigation machinery, aviation, national defense, automobile and other industries at home and abroad to produce steel, iron and non-ferrous carbon alloy castings. Among them, the production of castings such as centrifugal cast iron pipe, cylinder liner and shaft sleeve of internal combustion engine is the most common.
(6) Gravity die casting

Metal mold casting: refers to a molding method in which liquid metal fills the metal mold under the action of gravity and cools and solidifies in the mold to obtain castings.
Technological process:
Process characteristics
Advantage:
1. The thermal conductivity and heat capacity of metal mold are large, the cooling speed is fast, the casting structure is dense, and the mechanical properties are about 15% higher than those of sand mold castings.
2. Castings with high dimensional accuracy and low surface roughness can be obtained, and the quality stability is good.
3. Because the sand core is not used or rarely used, it can improve the environment, reduce dust and harmful gases and reduce labor intensity.
Disadvantages:
1. The metal mold itself has no air permeability, so certain measures must be taken to export the air in the mold cavity and the gas produced by the sand core;
2. The metal mold has no concession, and cracks are easy to occur when the casting solidifies;
3. The manufacturing cycle of metal mold is long and the cost is high. Therefore, only in mass production can it show good economic results.
Application: metal mold casting is not only suitable for mass production of non-ferrous alloy castings such as aluminum alloy and magnesium alloy with complex shape, but also suitable for production of iron and steel metal castings and ingots.
(7) Vacuum casting
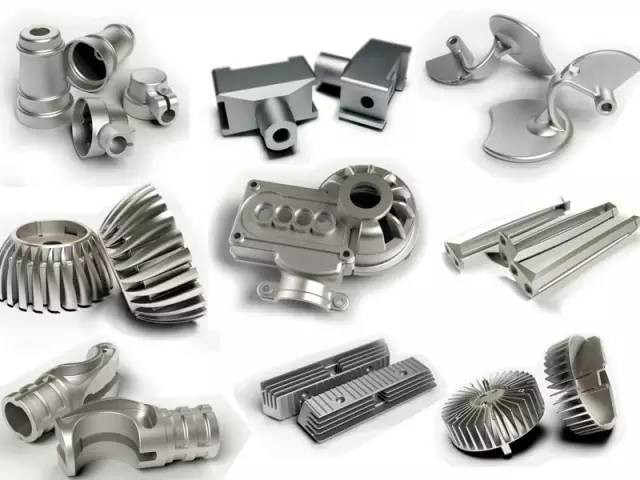

Vacuum casting: an advanced die casting process that eliminates or significantly reduces the pores and dissolved gases in the die castings by pumping out the gas in the die cavity during the die casting process, so as to improve the mechanical properties and surface quality of the die castings.
Technological process:
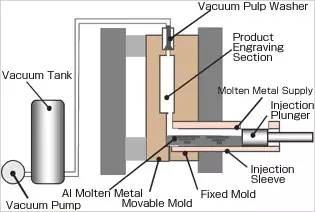
Process characteristics
Advantage:
1. Eliminate or reduce the air holes in die castings, improve the mechanical properties and surface quality of die castings, and improve the plating performance;
2. Reduce the back pressure of the mold cavity, use the alloy with low specific pressure and poor casting performance, and it is possible to die cast large castings with small machines;
3. The filling conditions are improved and thinner castings can be die cast;
Disadvantages:
1. The die sealing structure is complex, and it is difficult to manufacture and install, so the cost is high;
2. If the vacuum die casting method is not properly controlled, the effect is not very significant
(8) Squeeze die casting

Squeeze casting: it is a method of making liquid or semi-solid metal solidify and flow forming under high pressure to directly obtain parts or blanks. It has the advantages of high utilization rate of liquid metal, simplified process and stable quality. It is an energy-saving metal forming technology with potential application prospects
Technological process:
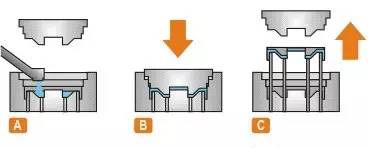
Direct squeeze casting: coating spraying, alloy pouring, mold closing, pressurization, pressure maintaining, pressure relief, mold splitting, blank demoulding and resetting;
Indirect squeeze casting: coating spraying, mold closing, feeding, mold filling, pressurization, pressure holding, pressure relief, parting, blank demoulding and resetting.
Technical features:
1. It can eliminate internal defects such as pores, shrinkage cavities and porosity;
2. Low surface roughness and high dimensional accuracy
3. It can prevent the occurrence of casting cracks;
4. It is convenient to realize mechanization and automation.
Application: it can be used to produce various types of alloys, such as aluminum alloy, zinc alloy, copper alloy, nodular cast iron, etc.
(9) Lost foam casting

Lost foam casting, also known as real mold casting, is a new type of casting method that combines the wax or foam model bonded to the size and shape of the casting into a model cluster. After coating the refractory coating and drying it, it is embedded in dry quartz sand in the vibration modeling, pouring under negative pressure, making the model gasified, the liquid metal occupies the mold position, and solidified and cooled to form a new casting method.
Process flow: pre foaming → foaming molding → coating dipping → drying → modeling → pouring → sand dropping → cleaning
Technical features:
1. The casting has high precision and no sand core, which reduces the processing time;
2. No parting surface, flexible design and high degree of freedom-
3. Clean production, no pollution;
4. Reduce investment and production costs.
Application: suitable for producing precision castings of various sizes with complex structure, unlimited alloy types and production batches. Such as gray cast iron engine box, high manganese steel elbow, etc.
(10) Continuous casting

Continuous casting: it is an advanced casting method. Its principle is to continuously pour the molten metal into a special metal mold called the mold, solidify (crusted) castings and continuously pull them out from the other end of the mold. It can obtain castings of any length or specific length.
Technological process:
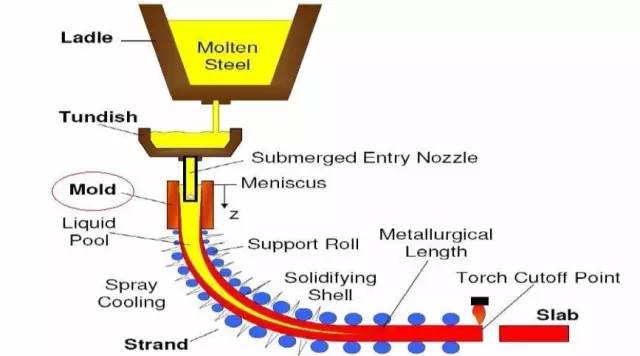
Technical features:
1. Because the metal is cooled rapidly, the crystal is dense, the structure is uniform and the mechanical properties are good;
2. Save metal and improve yield;
3. The process is simplified and the molding and other processes are avoided, so the labor intensity is reduced; The required production area is also greatly reduced;
4. Continuous casting production is easy to realize mechanization and automation and improve production efficiency.;
Application: continuous casting method can be used to cast long castings with unchanged section shape, such as steel, iron, copper alloy, aluminum alloy and magnesium alloy, such as ingot, slab, bar blank, pipe, etc.



