Melting Treatment Process of Ductile Iron and Matters Needing Attention
Alloying treatment of cast iron can be traced back to the 1930s and 1940s. Alloying treatment has made a qualitative leap in the properties of cast iron. At the same time, some special purpose cast iron such as wear resistance, corrosion resistance and heat resistance have also been born. It was also during this period that cast iron was produced by inoculation. In the late 1940s, the cast iron with spherical graphite after inoculation replaced the ordinary sheet graphite cast iron. We call this type of cast iron ductile iron.
Classification of spheroidizing and anti spheroidizing elements
Spherical elements are generally divided into three groups according to their spheroidizing effects.
The first group: Mg, Y, Ce, La, Pr, Sm, Dy, Ho, Er.
The second group: Ba, Li, Cs, Rb, Sr, Th, K, Na.
Group 3: Al, Zn, Cd, Sn.
The first group has the strongest spheroidizing ability, the second group takes the second place, and the third group is the weakest.
When magnesium is used as spheroidizing element, the third group of elements often produce anti spheroidizing effect.
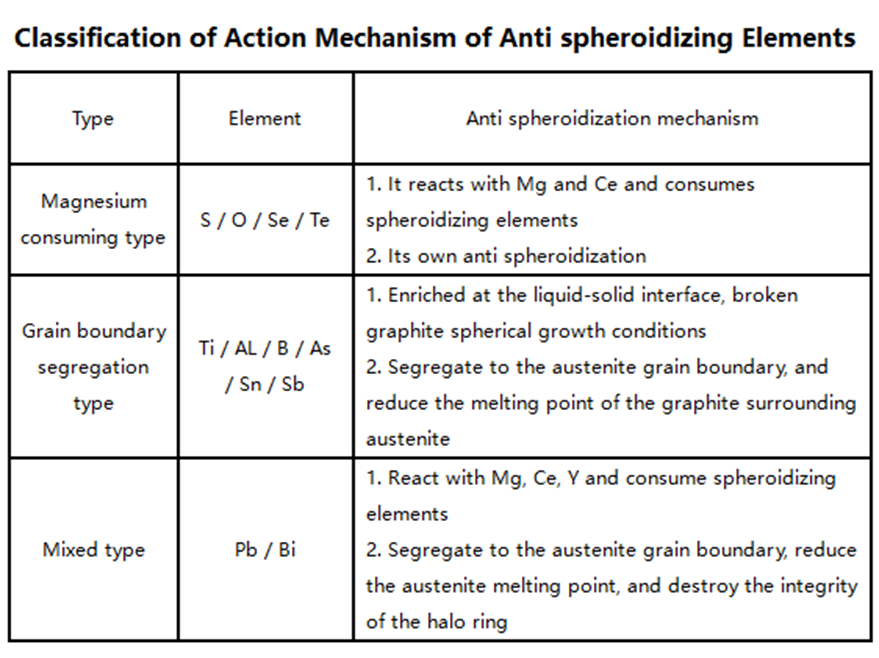
Anti spheroidizing elements: sulfur and oxygen are common anti spheroidizing elements in cast iron. In addition, Ti, Al, B, As, Pb, Sn, Sb, Bi, Te and Se are common anti spheroidizing elements in molten iron. The attached table is classified according to its action mechanism.
How to Select Spheroidizing Agent
Spheroidizing agent and inoculant are the most important materials in the process of spheroidizing treatment. In addition to stable quality, the following factors need to be considered when selecting a suitable spheroidizing agent.
Spheroidizing treatment temperature: if the spheroidizing treatment temperature is>1480 ℃, the spheroidizing reaction will be more intense, resulting in lower magnesium absorption. In order to make the spheroidizing reaction stable, spheroidizing agent with relatively high calcium content can be selected. If the spheroidizing temperature is less than 1480 ℃, spheroidizing agent with relatively low calcium content can be used.
Size of treatment package: If the height diameter ratio of the treatment package is 1:1, the loss of magnesium vapor will lead to the reduction of magnesium absorption, so it is recommended to use a nodulizer with high calcium content. If the height diameter ratio of the treatment package is 2:1, the spheroidizing reaction will be relatively stable, the magnesium vapor will diffuse into the molten iron, and the magnesium absorption rate will be improved.
Spheroidizing process: if the capping method is not used, the smoke generated by the spheroidizing reaction will enter the atmosphere and produce dazzling white light. In order to make the spheroidizing reaction stable, spheroidizing agent with low magnesium and high calcium can be used. If the capping process is used, the molten iron will not splash and will produce less smoke, the nodulizer with high magnesium and low calcium can be used to reduce the addition amount and nodulizing cost.
Treatment weight: if the weight of molten iron to be treated is less than 500kg, spheroidizing agent with smaller particle size can be used. It is recommended to use spheroidizing agent with particle size less than 12mm. If the weight of molten iron is 500~1000kg, spheroidizing agent with larger particle size can be used, such as 3~25mm spheroidizing agent. If the weight of treated molten iron is more than 1000kg, 4~32mm nodulizer can be used.
Silicon content: if the process yield of the casting products is low or the scrap rate is high, it is necessary to add more furnace charge and scrap steel for smelting, and the final casting has strict requirements on the silicon content of molten iron. On the premise that the inoculation amount can not be further reduced, low silicon nodulizer can be used for treatment, which can increase the return charge by 8%~15% and reduce the production cost of the foundry.
Sulfur content of raw iron liquid: If the sulfur content of raw iron liquid is high, if desulfurization treatment is not carried out, spheroidizing agent with high magnesium and high rare earth will be required, and the addition amount will be high. If the sulfur content of raw iron liquid is low, spheroidizing agent with low magnesium and low rare earth can be used, and the addition amount will be low, and the cost of spheroidizing agent with low magnesium and low rare earth will also be low.
Different spheroidizing methods
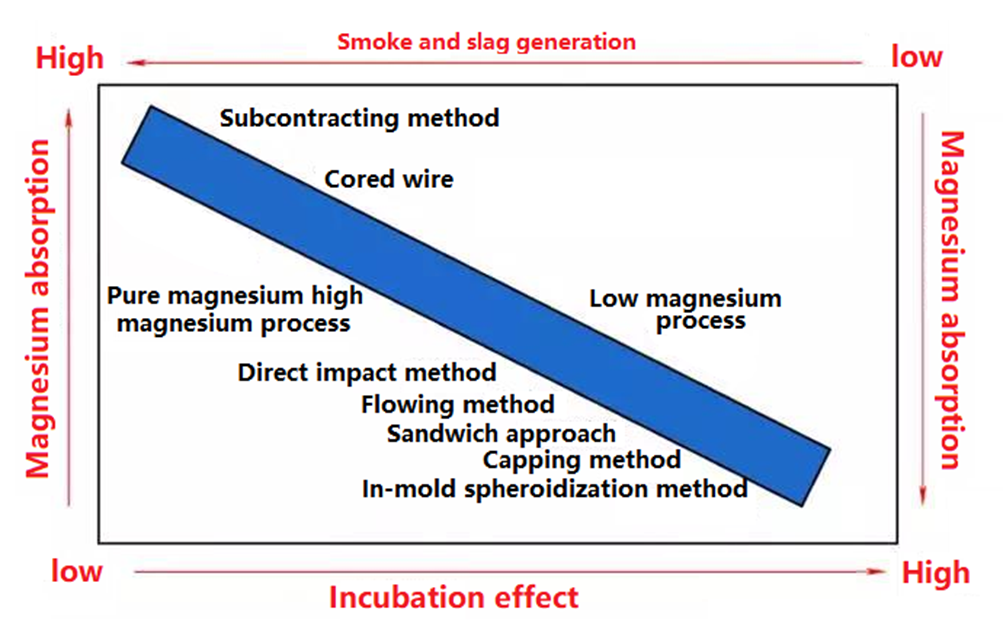
At present, the commonly used spheroidizing methods are as follows: in package processing (including direct punching, Sanmingzhi and capping), in mold spheroidizing, flowing, and pure magnesium processing (including subcontracting and cored wire). The advantages and disadvantages of these spheroidizing methods are briefly introduced below.
In bag processing: This is the most common spheroidizing process, which can be used in a wide range of applications, ranging from a few kilograms of auto parts to dozens of tons of wind power parts. The magnesium absorption rate of the capping method is the highest, followed by the Sanmingzhi method. The disadvantage is that the degree of automation is not high at present, and some domestic equipment factories are developing automatic feeding systems.
In mold spheroidizing method: there are not many foundries using this process now, because the disadvantages of this process are obvious. The slag generated by spheroidizing treatment sometimes enters the mold cavity, causing slag inclusion defects and waste products. In addition, this spheroidizing process requires high temperature and flow rate of molten iron, otherwise the spheroidizing will be uneven.
Flowing method: As the name implies, the flowing method is that molten iron flows through the spheroidizing chamber with spheroidizing agent to spheroidize. At present, this process does not use too much. The advantage is that the degree of automation is relatively high; The disadvantage is that the temperature and flow rate of molten iron are strictly required.
Pure magnesium spheroidizing process: sometimes called high magnesium spheroidizing process. At present, there are mainly two forms: subcontracting method and cored wire method. This method has the advantages of high automation and environmental protection; The disadvantage is that the magnesium absorption rate is low and more smoke and slag are generated.
Matters needing attention in production of nodular cast iron
Now briefly summarize the precautions for production of ductile iron.
(1) The sulfur content of molten iron and other trace elements should not be too high. If the content of sulfur and other trace elements in the molten iron is too high, more spheroidizing agents or spheroidizing agents with high rare earth content are required, so the cost of spheroidizing agents will increase. In addition, excessive spheroidizing agents will cause more slag, which is not conducive to the stability of casting quality. If the content of rare earth is too much, it is easy to produce fragmented graphite on castings with large section.
(2) Stability of spheroidizing treatment. The spheroidizing process is the key process in the production of ductile iron. Only when the spheroidizing process is stable can the quality of castings be stable. For different products and different sulfur content of molten iron, the amount of nodulizing agent and inoculant to be added shall be written into the operation instructions and strictly implemented.
(3) Avoid long waiting times. Pouring shall be carried out immediately after spheroidizing inoculation. As time goes on, the residual magnesium will be burned and the inoculation effect will decline.
(4) Avoid excessive residual magnesium content. Higher residual magnesium content will increase the shrinkage porosity tendency of castings. For general ductile iron, the residual magnesium content (mass fraction) should be controlled at 0.035%~0.045%, and for high nickel ductile iron, the residual magnesium content should be controlled at 0.06%~0.07%.
(5) Better inoculants shall be used for castings with higher requirements. For wind power components and high-speed iron components with high requirements, the stream inoculant with strong inoculation effect (such as patented Ultraseed/Ce) shall be selected. Its characteristic is that it can significantly increase the number of graphite spheres, and the graphite spheres are round.



